Understanding the Role and Functionality of Mud Pumps in Drilling Operations

Introduction to Mud Pumps
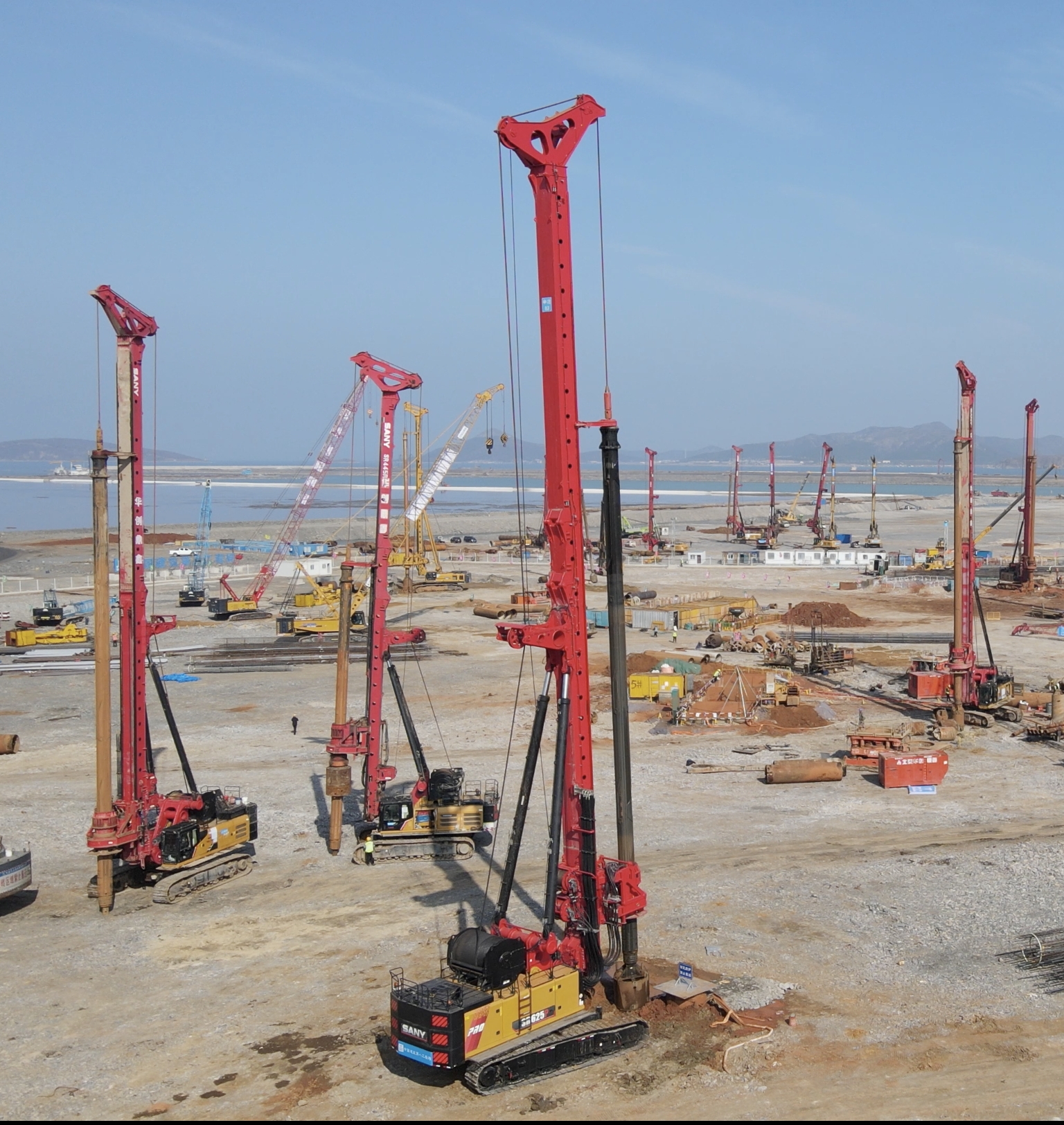
Mud pumps, also known as slurry pumps, are critical in the drilling industry. They are designed to circulate drilling fluid, or 'mud', which serves multiple purposes including cooling the drill bit, carrying cuttings to the surface, and maintaining hydrostatic pressure to prevent blowouts.
Types of Mud Pumps
There are primarily two types of mud pumps used in drilling operations: triplex pumps and duplex pumps. Triplex pumps, with three pistons, are more common due to their higher efficiency and ability to handle higher pressures. Duplex pumps, with two pistons, are simpler and easier to maintain but are less efficient.
Key Components and Functionality
The main components of a mud pump include the power end, fluid end, and the pulsation dampener. The power end converts the rotary motion of the engine into reciprocating motion, while the fluid end pressurizes and moves the drilling fluid. The pulsation dampener reduces pressure fluctuations to ensure a steady flow of mud.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of mud pumps. Common issues include wear and tear of the pistons and liners, which can lead to decreased performance. Routine inspections and timely replacement of worn parts can prevent costly downtime.
FAQs
What is the primary function of a mud pump?The primary function of a mud pump is to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure during drilling operations to cool the drill bit, remove cuttings, and maintain hydrostatic pressure.
How often should mud pumps be maintained?Mud pumps should undergo routine maintenance checks every 500 operating hours, with more thorough inspections every 2000 hours, depending on the operating conditions.
What are the signs of a failing mud pump?Signs of a failing mud pump include decreased flow rate, increased noise levels, and visible leaks. These symptoms indicate the need for immediate inspection and possible repairs.