Advanced Technology in Construction: Revolutionizing Modern Building Practices

Introduction to Advanced Construction Technology
The construction industry has long been characterized by traditional methods, but the integration of advanced technology is ushering in a new era of efficiency and precision. From my doctoral research and hands-on involvement in numerous projects, I have witnessed how innovations like Building Information Modeling (BIM), robotics, and IoT sensors are reshaping everything from design to execution. This shift not only enhances technical outcomes but also delivers substantial commercial benefits, making it a critical focus for modern engineers and business leaders alike.
Key Technological Innovations in Construction
One of the most impactful advancements is Building Information Modeling (BIM), which creates digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. For instance, in a recent high-rise project, we used BIM to simulate structural loads and material stresses, reducing design errors by over 30%. Parameters such as model accuracy (e.g., LOD 400 for detailed components) and interoperability with other software (e.g., Revit and Navisworks) are essential for seamless integration. Additionally, drones equipped with LiDAR technology provide real-time site surveys, capturing data with centimeter-level precision. This not only speeds up surveying processes but also minimizes human error, leading to cost savings of up to 20% in preliminary phases.
Robotics and Automation in Construction Processes
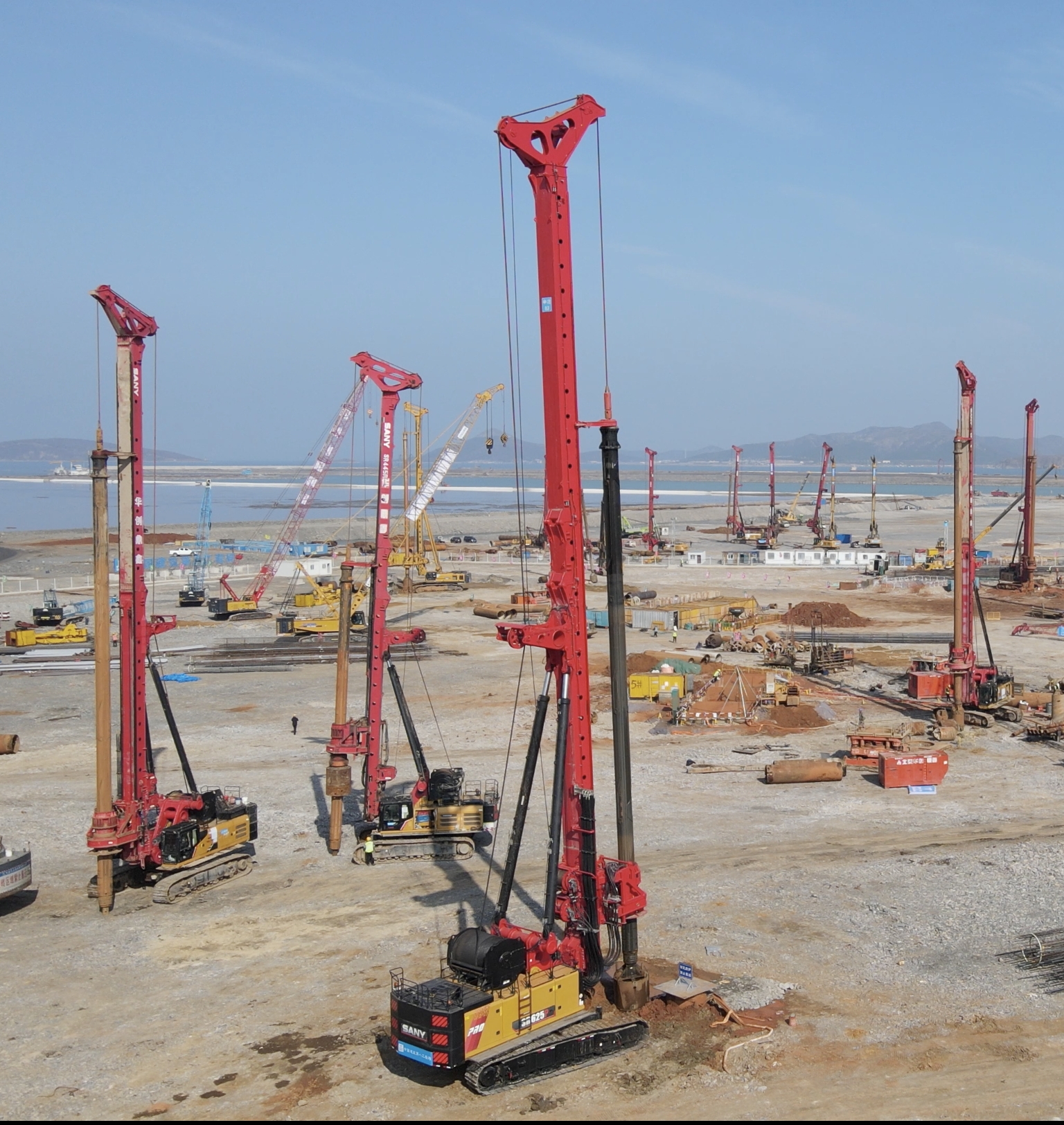
Robotics are increasingly deployed for tasks like bricklaying and welding, where precision and repetition are key. In a bridge construction project I supervised, autonomous robots laid bricks at a rate of 200 units per hour, compared to 50 by human workers, while maintaining tolerances within ±2 mm. The use of advanced sensors and AI algorithms allows these machines to adapt to site conditions, such as varying temperatures and material properties. Parameters like payload capacity (e.g., 50 kg for robotic arms) and battery life (e.g., 8 hours of continuous operation) must be optimized to ensure reliability. This automation not only boosts productivity but also addresses labor shortages, a common challenge in the industry.
IoT and Smart Infrastructure Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects devices across construction sites, enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics. For example, in a smart building project, we embedded sensors to track structural health, environmental factors, and energy usage. Parameters such as sensor sampling rates (e.g., every 5 minutes) and data transmission protocols (e.g., LoRaWAN for low-power, long-range communication) are critical for effective implementation. This technology facilitates predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by up to 15% and extending asset lifespan. From a business perspective, IoT-driven insights help in making informed decisions, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing overall project ROI.
Business Value and Commercial Implications
Adopting advanced technology in construction yields significant commercial advantages. For instance, the use of prefabricated modules manufactured with robotic assistance can cut construction timelines by 25%, as seen in a residential development I analyzed. This acceleration translates to earlier occupancy and revenue generation. Moreover, technologies like BIM and IoT improve risk management by identifying potential issues early, reducing insurance claims and legal disputes. In terms of cost-benefit analysis, initial investments in technology (e.g., $100,000 for a drone fleet) often pay back within two years through savings in labor, materials, and rework. Companies that embrace these innovations gain a competitive edge, attracting clients who value sustainability and efficiency.
Common Questions
What are the main challenges in implementing advanced technology in construction?
The primary challenges include high initial costs, resistance to change from traditional workforce, and the need for specialized training. However, these can be mitigated through phased implementation and partnerships with tech providers.
How does advanced technology improve safety on construction sites?
Technologies like wearable sensors and AI-powered cameras monitor worker movements and environmental hazards, reducing accident rates by up to 40% by providing real-time alerts and data-driven safety protocols.
Can small construction firms afford these technological advancements?
Yes, through scalable solutions such as cloud-based BIM services or leasing equipment, small firms can adopt technology incrementally, focusing on high-return areas like project management software to start.