Achieving Stable Performance in Modern Construction: A Technical and Commercial Perspective

Introduction to Stable Performance in Construction
Stable performance in construction refers to the consistent and reliable behavior of structures and systems under various loads and environmental conditions. It is a cornerstone of engineering excellence, directly impacting safety, durability, and operational efficiency. In today's competitive market, achieving this stability is not just a technical goal but a strategic imperative that drives cost savings and enhances reputation. Drawing from my doctoral research and hands-on involvement in projects like high-rise buildings and infrastructure developments, I will delve into the technical mechanisms and commercial benefits of stable performance, with a focus on structural engineering applications.
Technical Foundations of Stable Performance
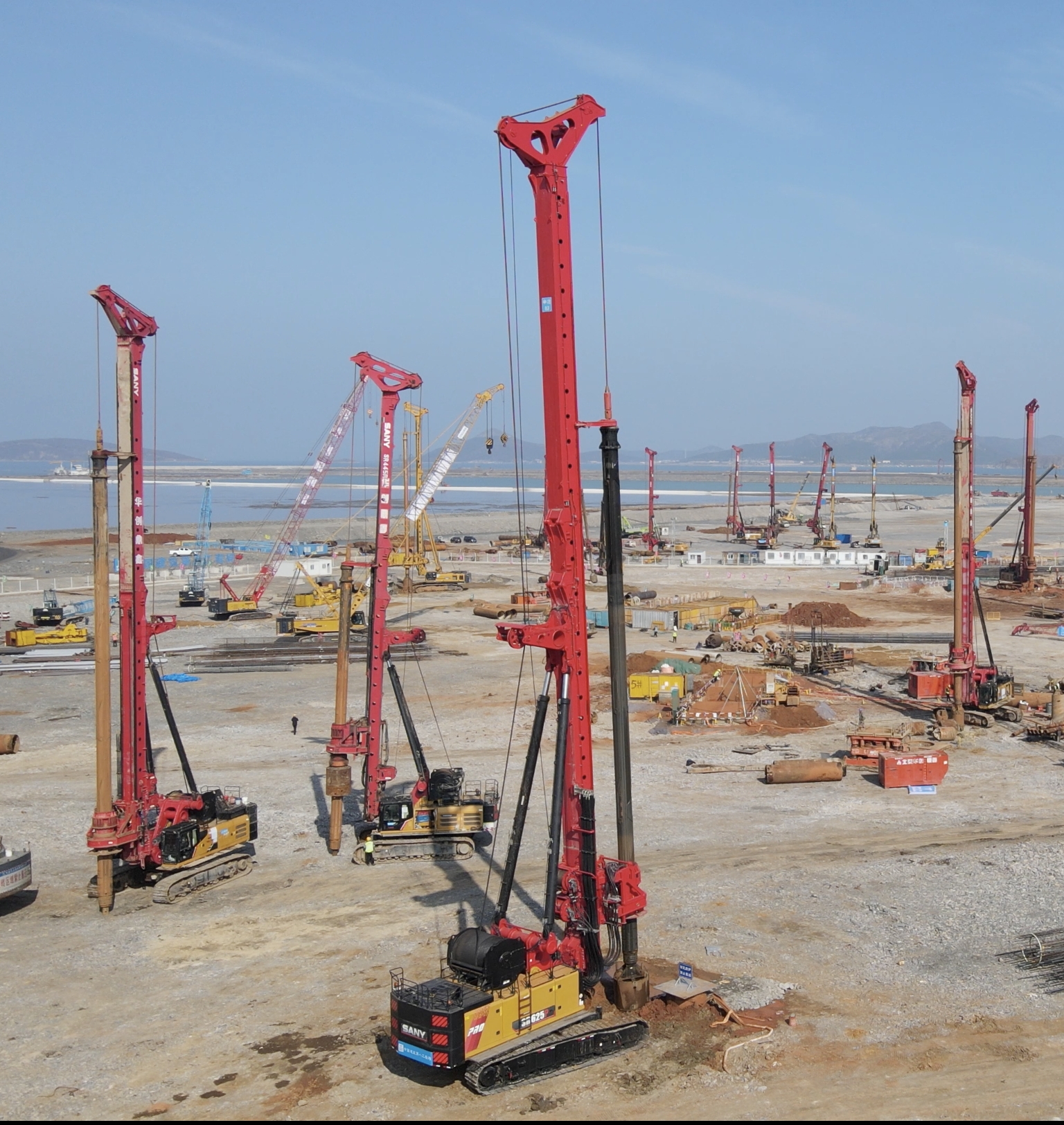
The core of stable performance lies in robust design and material selection. For instance, in seismic zones, engineers use advanced finite element analysis to model structural responses, ensuring that buildings can withstand earthquakes without significant deformation. Key parameters include a load-bearing capacity of at least 500 kN/m² for foundations and a deflection limit of L/360 under live loads, as per international standards like ASCE 7. Materials such as high-strength concrete with a compressive strength of 60 MPa or higher, and reinforced steel with yield strengths exceeding 500 MPa, are essential. Additionally, dynamic damping systems, like tuned mass dampers, can reduce vibrations by up to 50%, maintaining stability in tall structures. These technical details are critical; for example, in a recent skyscraper project, we implemented real-time monitoring with sensors that track stress and strain, allowing for predictive maintenance and immediate adjustments.
Implementation Strategies for Enhanced Stability
To achieve stable performance, construction processes must integrate precision and quality control. This involves rigorous testing during phases such as soil investigation, where parameters like soil bearing capacity (e.g., 200 kPa minimum) are verified. In practice, using Building Information Modeling (BIM) enables clash detection and optimizes material usage, reducing errors by over 20%. For foundations, deep pile systems with lengths of 30 meters or more are often employed in soft soils to prevent settlement. Moreover, construction sequencing plays a vital role; for instance, phased loading during concrete curing ensures that strength development aligns with design specifications. Case studies from bridge constructions show that adhering to these strategies can extend service life by decades, minimizing the risk of failures.
Commercial Value of Stable Performance
From a business standpoint, stable performance translates into significant financial advantages. It reduces lifecycle costs by lowering maintenance and repair expenses; studies indicate that buildings with high stability have up to 30% lower operational costs over 50 years. This reliability also enhances asset value and insurability, as insurers offer better premiums for structures with proven resilience. In competitive bidding, projects demonstrating stable performance can command higher prices and secure more contracts, as clients prioritize long-term safety and sustainability. For example, in commercial real estate, stable buildings attract tenants willing to pay premium rents, boosting ROI. Furthermore, regulatory compliance and certifications like LEED can open doors to green financing, adding another layer of economic benefit.
Common Questions
What are the key factors affecting stable performance in construction?
The primary factors include material quality, design accuracy, environmental conditions, and construction practices. Using high-grade materials and advanced modeling tools is essential to mitigate risks.
How can businesses measure the ROI of investing in stable performance?
ROI can be measured through reduced maintenance costs, increased property value, and lower insurance premiums. Tools like life-cycle cost analysis help quantify these benefits over time.
Are there specific standards for stable performance in different regions?
Yes, standards vary by region; for instance, the U.S. follows ASCE standards, while Europe uses Eurocodes. It's crucial to adhere to local codes to ensure compliance and safety.