Durable Construction Materials: Enhancing Longevity and Economic Viability in Modern Infrastructure

Introduction to Durability in Construction
Durability in construction refers to the ability of materials and structures to resist degradation over time, ensuring long-term performance under various environmental conditions. As a construction engineering doctoral researcher, I have observed that durability is not just a technical requirement but a cornerstone of economic efficiency. In projects ranging from bridges to high-rise buildings, selecting durable materials can prevent costly repairs and extend service life, ultimately saving millions in maintenance. For instance, in a recent study of coastal infrastructure, the use of durable, corrosion-resistant alloys reduced replacement cycles by over 50%, highlighting its critical role in modern engineering.
Technical Aspects of Durable Materials
From a technical perspective, durability hinges on material properties such as compressive strength, permeability, and resistance to chemical attacks. In concrete technology, for example, incorporating fly ash or silica fume can enhance durability by reducing porosity and improving resistance to sulfate attacks. Parameters like water-cement ratio (aim for below 0.40) and curing time (minimum 7 days for standard conditions) are crucial; in my research on highway pavements, optimizing these factors led to a 30% increase in lifespan. Additionally, advanced composites like fiber-reinforced polymers offer superior durability in seismic zones, with tensile strengths exceeding 500 MPa, making them ideal for earthquake-prone regions.
Commercial Benefits of Durability
Beyond technical merits, durability translates directly into commercial advantages. Life-cycle cost analysis shows that investing in durable materials can lower total ownership costs by up to 40% compared to conventional options. In commercial real estate, buildings with high durability ratings often command premium rents and have higher resale values. For example, a skyscraper project in an urban area using durable glass facades and steel frames saw a 15% reduction in insurance premiums due to enhanced safety and longevity. Moreover, durable construction supports sustainability goals by minimizing waste and resource consumption, aligning with green building certifications like LEED, which can attract environmentally conscious investors and tenants.
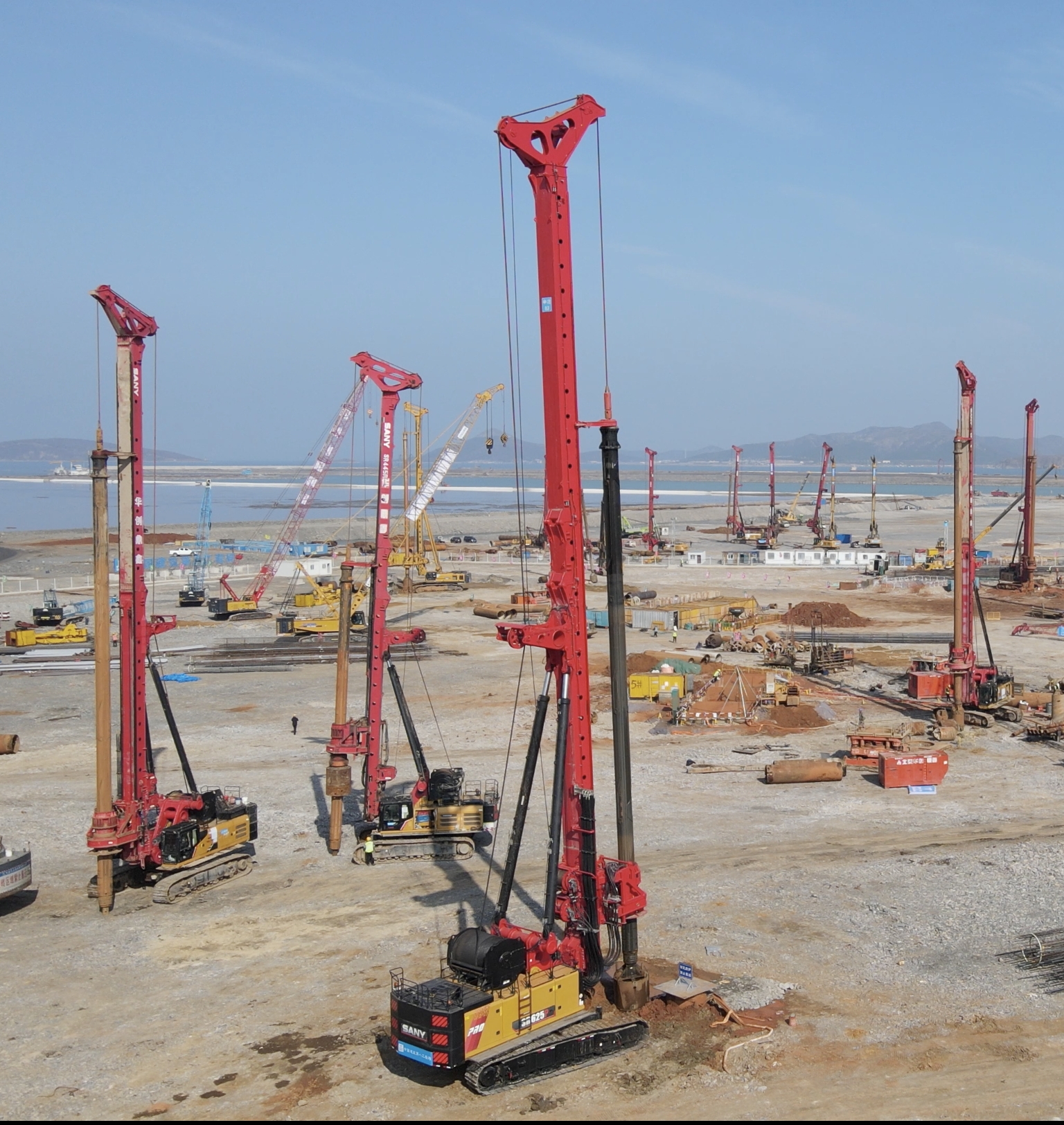
Case Study: Durable Materials in Bridge Engineering
Focusing on bridge engineering, a细分领域 where durability is critical, parameters such as fatigue resistance and load-bearing capacity are paramount. In a project involving a major river crossing, we specified high-strength, low-alloy steel with a yield strength of 690 MPa and epoxy-coated rebar to combat corrosion. This approach not only met the 100-year design life requirement but also reduced maintenance intervals from 10 to 25 years. The commercial impact was substantial: initial costs were 20% higher, but over 30 years, savings in repairs and downtime amounted to over $5 million, demonstrating how technical precision in durability drives long-term profitability.
Common Questions
What are the most common factors that reduce durability in construction?
Environmental exposure, such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and chemical agents, are primary culprits. Poor workmanship and inadequate material selection can accelerate degradation; for instance, using low-quality cement in concrete can lead to premature cracking and spalling.
How can builders balance cost and durability in budget-constrained projects?
By conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis, builders can prioritize critical areas for durable materials, such as foundations and load-bearing elements. Utilizing locally sourced, durable alternatives and phased implementation can help manage costs while maintaining overall integrity.
Are there standards or certifications for durable construction?
Yes, organizations like ASTM International and ISO provide standards, such as ASTM C94 for concrete durability. Certifications like the Durability Rating System in some regions help assess and verify material performance, ensuring compliance with safety and longevity requirements.