Durability in Construction: Enhancing Longevity and Economic Value in Modern Infrastructure

Introduction to Durability in Construction
Durability refers to the ability of a construction material or structure to resist deterioration over time due to environmental factors such as weather, chemical exposure, and mechanical loads. In modern engineering, achieving high durability is not just about longevity but also about reducing lifecycle costs and enhancing safety. For instance, in bridge construction, durable materials like high-performance concrete can prevent costly repairs and extend service life by decades. This section explores the fundamental principles and why durability is critical in today's fast-paced construction industry.
Technical Aspects of Enhancing Durability
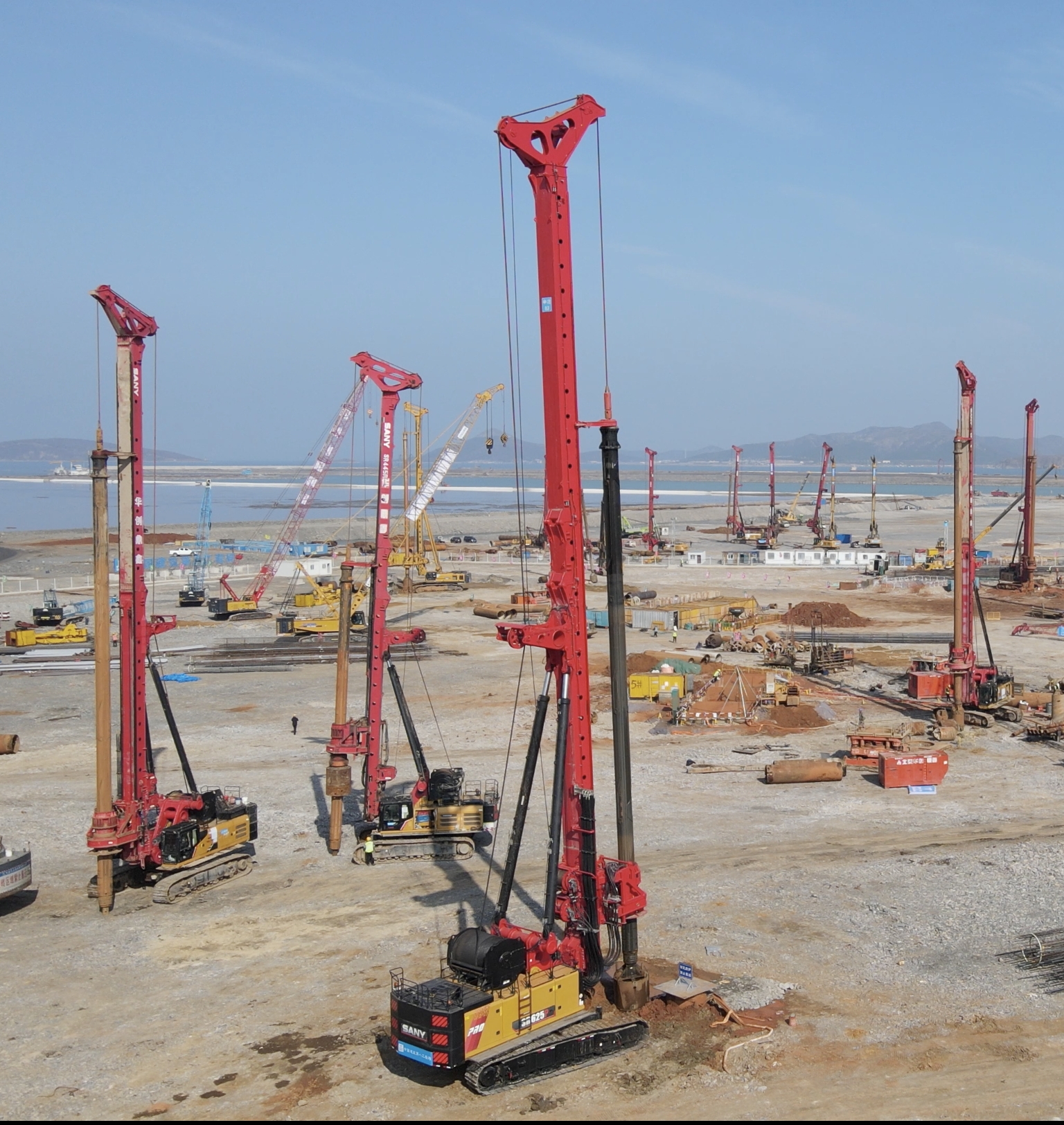
To improve durability, engineers focus on material properties and design considerations. Material selection is paramount; for example, using corrosion-resistant steel or fiber-reinforced polymers can significantly reduce degradation. In concrete structures, parameters like water-cement ratio (aim for 0.4 or lower) and the use of admixtures such as silica fume enhance compressive strength and resistance to sulfate attack. Additionally, protective coatings and cathodic protection systems are employed to shield against environmental hazards. Case studies from projects like the Burj Khalifa demonstrate how advanced materials and rigorous testing protocols ensure structures endure harsh climates, with durability factors exceeding 50 years under extreme conditions.
Business Value of Durable Construction
Investing in durability yields substantial economic benefits. Lifecycle cost analysis shows that while initial costs may be higher, durable constructions lead to lower maintenance, repair, and replacement expenses over time. For businesses, this translates to improved return on investment (ROI) and enhanced asset value. In commercial real estate, durable buildings attract tenants and command higher rents due to reduced downtime and reliability. Moreover, regulatory compliance and sustainability certifications, such as LEED, often prioritize durability, opening doors to tax incentives and green funding. By integrating durability into project planning, companies can mitigate risks and build a reputation for quality, as seen in infrastructure projects that secure long-term public-private partnerships.
Common Questions
What are the key factors affecting durability in construction?
Key factors include material quality, environmental exposure, design accuracy, and maintenance practices. For example, in coastal areas, salt spray can accelerate corrosion, so using stainless steel or protective coatings is essential.
How can businesses justify the higher upfront costs of durable materials?
Through detailed cost-benefit analyses that highlight long-term savings. For instance, durable roofing materials may cost 20% more initially but can save up to 50% in maintenance over 30 years, making them a wise investment.